Diabetes Insipidus Lab Tests
Water deprivation test a water deprivation test involves not drinking any liquid for several hours to see how your body responds. if you have diabetes insipidus, you'll continue to pee large amounts of dilute urine when normally you'd only pee a small amount of concentrated urine. during the test, the amount of urine you produce will be measured. Tests and diagnosis discussion for diabetes insipidus: because dm is more common and because dm and di have similar symptoms, a health care provider may suspect that a patient with di has dm. but testing should make the diagnosis clear.
Diagnosing Canine Diabetes Insipidus Vetinfo

Diabetesinsipidus knowledge for medical students and.
Diabetesinsipidus (die-uh-bee-teze in-sip-uh-dus) is an uncommon disorder that causes an imbalance of fluids in the body. this imbalance makes you very thirsty even if you've had something to drink. it also leads you to produce large amounts of urine. while the terms "diabetes insipidus" and "diabetes mellitus" sound similar, they're not related. The main reason this test is ordered is to see if you are suffering from central diabetes insipidus — a disease that causes excessive urination. the test is based on a lab analysis of your. Clinical trials. explore mayo clinic studies testing new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this disease.. lifestyle and home remedies. if you have diabetes insipidus: prevent dehydration. diabetes insipidus lab tests as long as you take your medication and have access to water when the medication's effects wear off, you'll prevent serious problems.

The water deprivation test and a potential role for the arginine vasopressin precursor copeptin to differentiate diabetes insipidus from primary polydipsia. endocr connect 2015; 4:86. fenske w, allolio b. clinical review: current state and future perspectives in the diagnosis of diabetes insipidus: a clinical review. What is diabetes insipidus? diabetes insipidus is a rare condition that causes your body to make a lot of urine that is "insipid," or colorless and diabetes insipidus lab tests odorless. most people pee out 1 to 2 quarts a. Pathophysiology diabetes insipidus refers to the condition where the kidneys are unable to retain water. even though the patient may be dehydrated, the kidneys cannot balance the fluid and produce large amounts of insipid urine (dilute and odorless). the kidneys normally produce 1-2 quarts of urine per day, but with diabetes insipidus, they may produce
In a patient whose clinical presentation suggests diabetes insipidus (di), laboratory tests must be performed to confirm the diagnosis. a 24-hour urine collection for determination of urine volume is required. in addition, the clinician should measure the following:. Treatment options for the most common types of diabetes insipidus include: central diabetes insipidus. if you have mild diabetes insipidus, you may only need to increase your water intake. if the condition is caused by an nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. since the kidneys don't properly respond. 5. maghnie m, cosi g, genovese e, et al. central diabetes insipidus in children and young adults. n engl j med. 2000; 343(14): pp. 998–1007. doi: 10. 1056/nejm200010053431403. 6. mao jf, zhang jl, nie m, lu sh, wu xy. diabetes insipidus as the first symptom caused by lung cancer metastasis to the pituitary glands: clinical presentations. A disorder similar to diabetes mellitus in that it causes symptoms such as increased thirst and increased urine production, but differing in cause, frequency, treatment and associated complications; diabetes insipidus results from a lack of production of arginine vasopressin (also called antidiuretic hormone or adh) by the pituitary or a lack of response of the kidneys to adh, causing an.
Diabetesinsipidus (di) is a condition characterized by large amounts of dilute urine and increased thirst. the amount of urine produced can be nearly 20 liters per day. reduction of fluid has little effect on the concentration of the urine. complications may include dehydration or seizures.. there are four types of di, each with a different set of causes. Diabetesinsipidus (di) is defined as the passage of large volumes (>3 l/24 hr) of dilute urine (< 300 mosm/kg). it diabetes insipidus lab tests has the following 2 major forms: central (neurogenic, pituitary, or neurohypophyseal) di, characterized by decreased secretion of antidiuretic hormone (adh; also referred to as arginine vasopressin [avp]) nephrogenic di, charac. Blood test results for diabetes insipidus. what you can anticipate. the glucose tolerance test is carried out in a number of steps. when you reach your medical professional’s office or lab, a member of your health care group will take a sample of blood from a vein in your arm.
Diabetesinsipidus A Review Medscape
Only a laboratory testing is able to confirm the presence of diabetes insipidus. these tests in some form have been available in the united states since the 1930s. if the clinical presentation of this condition is suggested by the signs and symptoms being suffered, then a medical provider will order a 24 hour urine collection Which laboratory test result should the nurse expect in a patient with alcoholic ketoacidosis? below normal to slightly elevated serum glucose level. diabetes insipidus. in a patient with diabetic ketoacidosis, the nurse should expect which laboratory finding?. Laboratory studies the diagnosis of diabetes insipidus (di) is often made clinically, while the laboratory tests provide confirmation. perform testing with the patient maximally dehydrated as tolerated, that is, at a time when adh release would be highest and urine would be most concentrated. Diabetes insipidus (die-uh-bee-teze in-sip-uh-dus) is an uncommon disorder that causes an imbalance of fluids in the body. this imbalance makes you very thirsty even if you've had something to drink. it also leads you to produce large amounts of urine. while the terms "diabetes insipidus" and "diabetes mellitus" sound similar, they're not related.
Diabetes insipidus lab tests online au. site map of article content. glossary. diabetes insipidus. a disorder similar to diabetes mellitusin that it causes symptoms such as increased thirst and increased urine production, but differing in cause, frequency, treatment and associated complications; diabetes insipidus results from a lack of production of arginine vasopressin (also called antidiuretic hormone or adh) by the pituitary or a lack of response of the kidneys to adh, causing an. Diabetesinsipidus is a rare disorder that occurs when a person's kidneys pass an abnormally large volume of urine that is insipid—dilute and odorless. in most people, the kidneys pass about 1 to 2 quarts of urine a day. in people with diabetes insipidus, the kidneys can pass 3 to 20 quarts of urine a day.
A blood test involves drawing a patient's blood at a health care provider’s office or a commercial facility and sending the sample to a lab for analysis. the blood test measures sodium levels, which can help diagnose diabetes insipidus and in some cases determine the type. Differential diagnosis includes nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, neurogenic/central diabetes insipidus and psychogenic polydipsia. they may be differentiated by using the water deprivation test. recently, lab assays for adh are available and can aid in diagnosis.
The water deprivation test helps the vet diagnose whether the disease is central diabetes insipidus or nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. administration of synthetic vasopressin can confirm central diabetes insipidus, because this hormone will cause a decrease in polyuria and polydipsia. In a patient whose clinical presentation suggests diabetes insipidus (di), laboratory tests must be performed to confirm the diagnosis. a 24-hour urine collection for determination of urine volume.
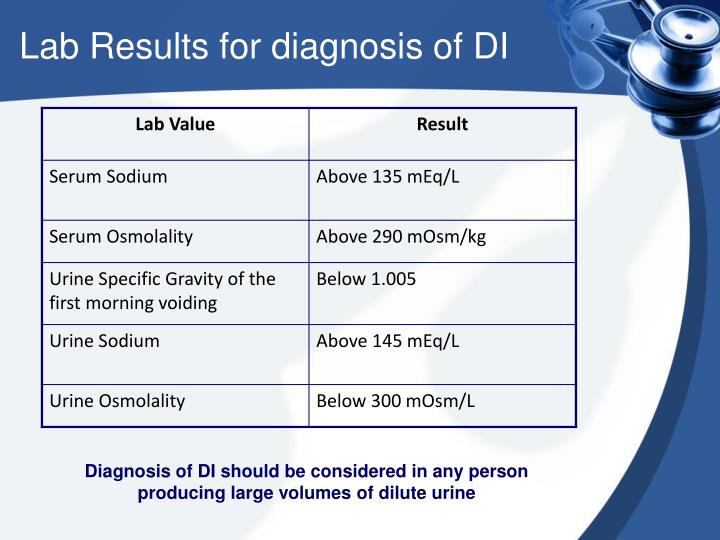
If the urine has a specific gravity of 1,005 or less, then this can indicate the presence of this health condition. urinary osmolality that is less than 200 mosm/kg is also a strong indicator of the presence of diabetes insipidus. the average plasma osmolality on a random patient test is 287 mosm/kg of water. if there are large volumes of urine that is very dilute or clear, then this can be a visual indicator that these testing values may be present. Anti-saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies (asca) antibiotic susceptibility testing. anticentromere antibody. antidiuretic hormone (adh) antimitochondrial antibody and ama m2. If you have diabetes insipidus, your urine will be very dilute, with low levels of other substances. a large amount of sugar in your urine may be a sign of type 1 or type 2 diabetes rather than diabetes insipidus. vasopressin test. after the water deprivation test, you may be given a small dose of avp, usually as an injection. Diabetesinsipidus results from a deficiency of vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone [adh]) due to a hypothalamic-pituitary disorder (central diabetes insipidus) or from resistance of the kidneys to vasopressin (nephrogenic diabetes insipidus). polyuria and polydipsia develop. diagnosis is by water deprivation test showing failure to maximally concentrate urine; vasopressin levels and response to.
Blood test results for diabetes insipidus diabetesbros.
Comments
Post a Comment